
It may be time to get your hearing checked. AARP Hearing Solutions makes it simple. Find a provider today.
Wondering how much earwax is too much? Get expert advice on the telltale signs, how to clean your ears safely and more.
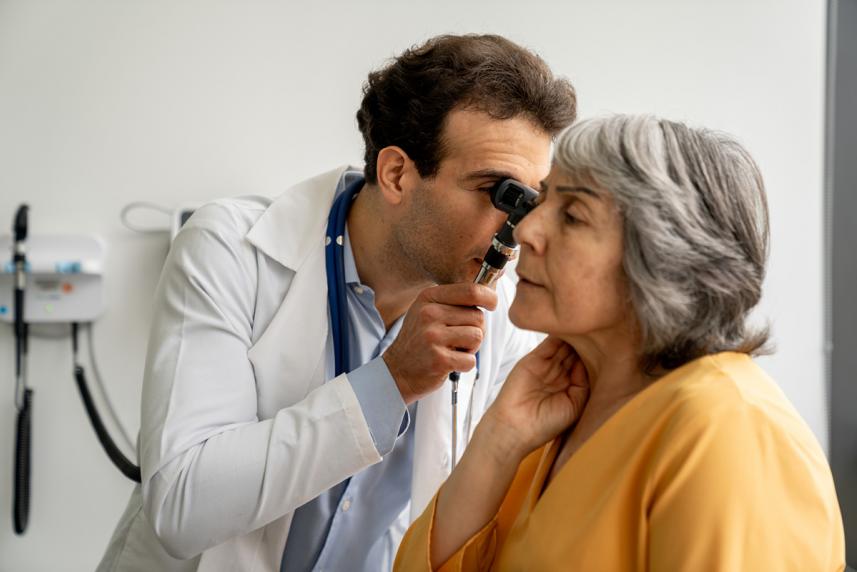
Earwax may look gross, but it’s actually a good thing. This sticky substance moisturizes the insides of your ear canal. It helps fight off infection by trapping dust and other things. And it also has antibacterial and water-resistant properties.1
But even though it’s normal, patients often have questions about it, says Melanie Vazquez, an audiologist at Swedish Audiology Services in Seattle. They may wonder how much earwax is too much, for instance. Other common questions include whether hearing aids cause earwax issues and how to clean your ears, she adds.
You may wonder about earwax too. Here are some answers to the most common questions, from how often to clean your ears to how to do it safely — and everything in between.

It may be time to get your hearing checked. AARP Hearing Solutions makes it simple. Find a provider today.
Not at all. Everyone’s ears produce earwax. And most of the time, your ears do a good job of cleaning themselves. Earwax moves along the ear canal until it falls out or washes away.
Some people, though, produce more earwax. This is usually due to things that they can’t control, like their genes or how much ear hair they have.2
So how much earwax is too much? When a hearing care professional or your primary care provider (PCP) can still see your ear drum during an ear exam, then it’s not an issue, explains Vazquez. But if they can only see some of the ear drum, then it may be time to remove the excess wax — either professionally or safely at home.
Earwax can become hard, making it tough to wash away. That may make your ears hurt. Some other signs include:3, 4
If you’re a hearing aid wearer, you may start hearing a lot of feedback, squealing or whistling from the hearing aid, says Vazquez. Or your device may not work as well. If that’s the case, see your hearing care professional. They can check if you have impacted earwax.
Did you know that you may be able to request a no-cost hearing exam and consultation through AARP® Hearing Solutions™ provided by UnitedHealthcare Hearing? Request an appointment.
They might. “Wearing hearing aids may not necessarily increase wax production but can sometimes increase the chances for buildup,” says Vazquez. The reason? Hearing aids sometimes prevent earwax from flowing out of the ear canal naturally — especially in people who produce more earwax, she explains.
If that’s the case for you, Vazquez suggests regular cleanings by an expert. You can see an ear, nose and throat doctor (ENT), your PCP or a hearing care professional like an audiologist. They can also let you know how to clean your ears safely at home, she adds.
And remember to clean your hearing aids every day, notes Vazquez. Your hearing care professional will show you how to do it.
Because cotton swabs can push earwax back into the ear canal and potentially cause blockage, says Vazquez. Push a swab in far enough, and it may even rupture your eardrum. Or damage the fragile skin inside the ear and cause an infection.4
Yes. These drops work well to dissolve excess earwax, especially if you have a small amount. Look for drops that contain carbamide peroxide or other types of peroxide.4
Tilt your head to one side and put the drops in the ear that’s facing up. Then lie down on your side for 5 minutes. When you sit up, the drops plus earwax should run out of your ear. You can then wipe the outer ear with a moist towel or washcloth.
The bottom line? Earwax is nothing to be alarmed about. Even if you do produce a lot of it, or wear hearing aids, it can be taken care of pretty easily.
Sources
Information is for educational purposes only and is not a substitute for the advice of a licensed medical provider. Consult your provider prior to making changes to your lifestyle or health care routine.
AARP Hearing Solutions is available to all AARP members and does not require a health insurance plan from UnitedHealthcare. The AARP hearing program discount cannot be combined with any other discounts, promotions, coupons or hearing aid benefit plans unless noted herein. Products or services that are reimbursable by federal programs including Medicare and Medicaid are not available on a discounted or complimentary basis. AARP commercial member benefits are provided by third parties, not by AARP or its affiliates. Providers pay a royalty fee to AARP for the use of its intellectual property. These fees are used for the general purposes of AARP. Some provider offers are subject to change and may have restrictions. Please contact the provider directly for details. UnitedHealthcare Hearing is provided through UnitedHealthcare, offered to existing members of certain products underwritten or provided by UnitedHealthcare Insurance Company or its affiliates to provide specific hearing aid discounts. This is not an insurance nor managed care product, and fees or charges for services in excess of those defined in program materials are the member's responsibility. UnitedHealthcare does not endorse nor guarantee hearing aid products/services available through the hearing program. This program may not be available in all states or for all group sizes. Components subject to change.
Network size varies by market.